

Isn't it ideal to anticipate the iceberg before colliding with it? – Kattia Ramírez, CEO QF Nexus.

Effective management makes it possible to identify, measure, and control risks, reducing potential losses, which protects shareholders' capital.
Compliance with applicable laws and regulations by local and international regulators helps avoid costs associated with litigation, fines, and sanctions.
A company or financial institution that demonstrates good risk management generates greater trust among its customers and in the market, which not only attracts investors but also strengthens its reputation with stakeholders.

Controlling risks reduces exposure to disruptive events, minimizing volatility in financial results and increasing resilience to economic crises.
Early identification of risks makes it possible to make informed strategic decisions based on data and analysis, which simultaneously allows you to prioritize and allocate resources more efficiently.
Proper risk management allows you to identify and take advantage of situations that can generate benefits for the organization, including: detecting areas for improvement, anticipating trends, and fostering innovation.
At QF Nexus, we are ready to support you in taking safe steps toward efficient and effective risk management so that you can focus on growing your business.

We transform the complexity of risk management into clear vocabulary and easily understandable strategies that allow you to move forward with confidence in increasingly volatile and complex environments.
We make risk management backed by vision, strategic integration, business knowledge, and proactivity, so that decision-making is timely, effective, and aligned with the strategy.


We take your risk management to the next level with simple yet robust solutions that generate short-term value and are continuously improved through experience and the learning process.
Diagnosis, assessment, methodology development, and implementation of best practices regarding:
Training for related bodies on corporate governance, regulatory compliance, and performance evaluation.
We offer you services to strengthen each of the risk management stages:
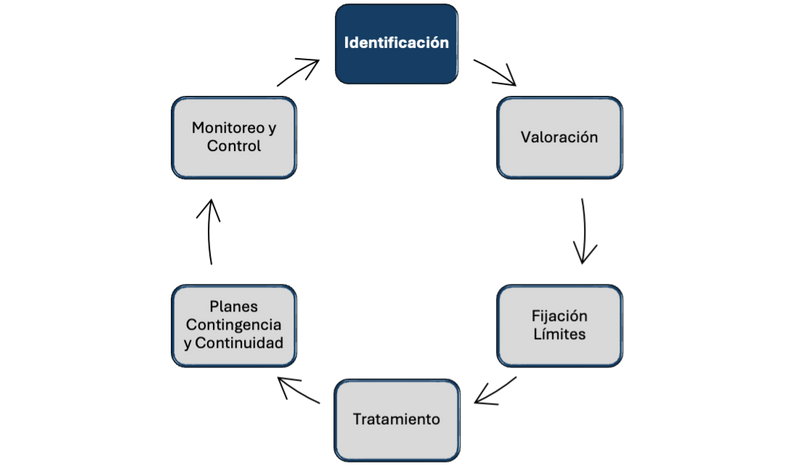
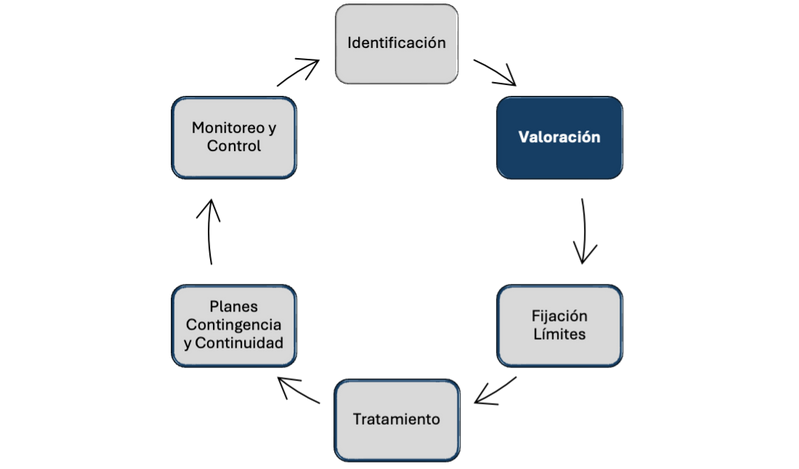
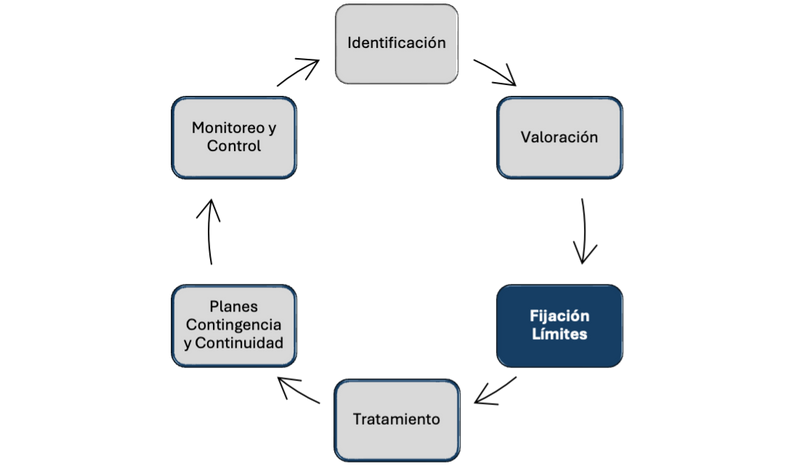
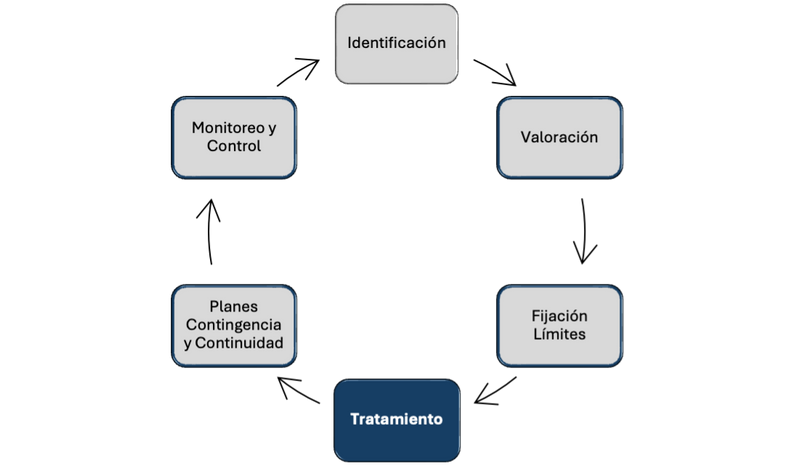
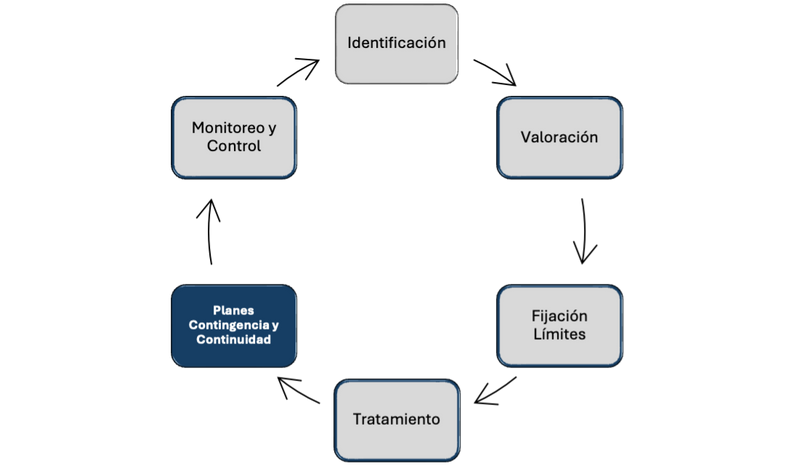
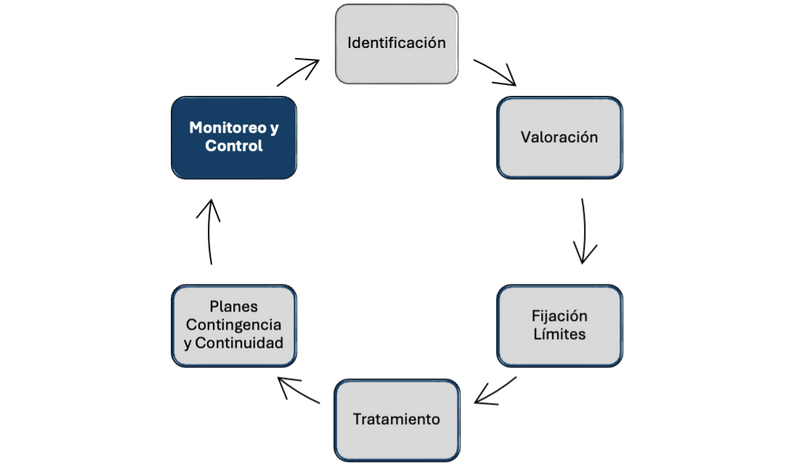

Development of Recovery Indicators (RI): Creation of specific metrics to measure financial stability, liquidity, capitalization, and profitability, acting as early warning signals of deterioration.
Stress scenario simulation: Evaluation of plan effectiveness through stress testing and sensitivity analysis addressing hypothetical extreme stress situations.
Identification of critical functions: Determining which operations and services must be maintained during a resolution to avoid impacts on the financial system.
Structuring resolution plans: Advising the organization on the development of resolution plans in accordance with regulations.


“In the business world, the rearview mirror is always clearer than the windshield.”
Did you know that it is estimated that the marine world contains more than 500 thousand animal species? However, about 230 thousand species have been identified, and among them we share some curiosities:
Dolphin: Considered the most intelligent marine animal, demonstrated by problem-solving capacity, communication, and social learning.
Icelandic clam: This mollusk can live more than 500 years, as shown by the specimen called “Ming,” which is estimated to have been 507 years old when discovered.
Octopus: Considered the most resilient and strategic animal in the sea. It can change color and texture depending on the environment and can learn new skills quickly.
The marine world is an ideal scenario to exemplify that risk management must be intelligent, continuous, resilient, and strategic.